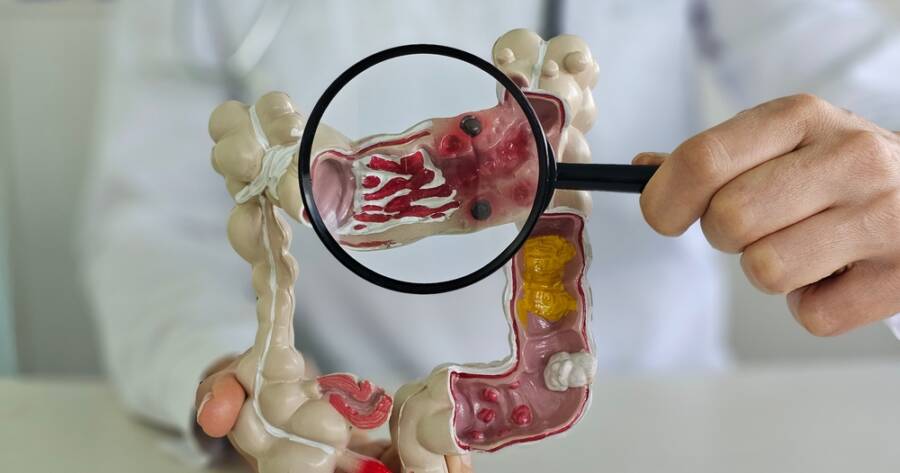
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the colon and rectum, leading to prolonged inflammation and ulcer formation in the digestive tract. It can significantly impact quality of life, necessitating effective management strategies for those living with the condition. By understanding the symptoms and exploring comprehensive treatment options, individuals with UC may find a path to relief and improved health. Awareness and proactive management are key to navigating this complex condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis presents itself through a range of symptoms that can vary in severity. Common signs include persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, and cramping, often accompanied by blood in the stool. These symptoms may escalate during flare-ups, with episodes leading to increased urgency and frequency of bowel movements. Fatigue, weight loss, and fever are also possible, resulting from the body’s response to inflammation.
It’s important to note that symptoms may present gradually and can vary from mild to severe. Chronic UC can lead to complications such as anemia or dehydration, further affecting daily life. Early recognition of these symptoms and seeking medical advice are crucial in addressing the condition proactively. Open dialogue with healthcare providers ensures timely evaluations and appropriate interventions.
Understanding the Causes
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. The immune system’s response is a significant element, where an abnormal reaction potentially targets the cells lining the colon. This misguided immune attack leads to inflammation and ulceration, affecting bowel function and causing significant discomfort.
Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role, as individuals with a family history of UC or other autoimmune conditions might have increased susceptibility. Environmental factors such as diet, stress, and use of certain medications can influence symptom severity or trigger flare-ups. Recognizing these potential contributors supports effective management and aids in reducing exacerbation likelihood.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing ulcerative colitis requires a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. A comprehensive medical history and physical examination offer a foundation for identifying potential UC symptoms. Laboratory tests, including blood work, can reveal anemia or inflammation, supporting an ulcerative colitis diagnosis.
Endoscopic procedures, such as colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, enable direct examination of the colon lining, confirming inflammation presence and extent. These tests allow for biopsy collection, providing additional insights into the disease’s nature. The integration of imaging studies, like CT scans or MRIs, may also assist in assessing the severity of UC and ruling out other conditions. Early and accurate diagnosis guides effective treatment strategies.
Current Treatment Options
Management of ulcerative colitis involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs and disease severity. Medications form the foundation of treatment, aiming to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and induce remission. Aminosalicylates and corticosteroids are commonly used anti-inflammatory drugs, providing relief during flare-ups.
Immunosuppressants may be prescribed to control or prevent immune system attacks, reducing inflammation and promoting remission. Biologic therapies, targeting specific proteins involved in inflammation, have gained traction for individuals unresponsive to conventional treatments. Close monitoring by healthcare specialists remains vital to adjust medication plans and optimize outcomes.
Complementary Therapies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Complementary therapies and lifestyle adjustments can support medical treatments in managing ulcerative colitis. Nutritional guidance focuses on identifying and avoiding trigger foods, reducing symptom exacerbation, and ensuring adequate nutrient intake. Staying hydrated and following a balanced diet bolsters overall health and supports the digestive system.
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or tai chi, can aid in reducing symptom flare-ups linked to stress. Regular exercise strengthens the body and enhances mood, contributing to overall well-being. Engaging with support groups or counseling services provides emotional support and insights from others living with UC, fostering resilience and shared experiences.
Surgical Intervention Considerations
In cases where ulcerative colitis does not respond to medication, surgical intervention might be considered. Surgery involves removing the colon affected by inflammation, offering a potential solution for severe cases. Total proctocolectomy, the removal of both the colon and rectum, may permanently alleviate symptoms and eliminate the need for further medical treatments.
Pouch surgery, forming a new pouch from small intestine tissue, allows for waste elimination without an external bag, enhancing post-surgical quality of life. The decision to pursue surgery requires careful consultation with healthcare providers, weighing potential benefits against inherent risks. For some, surgical collaboration becomes a meaningful component of comprehensive UC management.
Taking Control of Ulcerative Colitis
Managing ulcerative colitis is an ongoing journey requiring a comprehensive understanding of symptoms and treatment options. Through a combination of medical therapies, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, surgical interventions, individuals can effectively reduce symptoms and achieve long-term remission.
Partnering with healthcare providers and creating a personalized management plan fosters empowerment and informed decision-making. Embracing a proactive approach can lead to improvements in quality of life, offering hope and encouragement in navigating this chronic condition. Continual learning and engagement pave the way for effective control of UC, enhancing well-being and overall health through every stage of life.